Tuberculin Skin Test
Test Overview
A tuberculin skin test (also called a Mantoux tuberculin test) is done to see if you have ever been exposed to tuberculosis (TB). The test is done by putting a small amount of TB protein (antigens, Opens dialog) under the top layer of skin on your inner forearm. If you have ever been exposed to the TB bacteria (Mycobacterium tuberculosis), your skin will react to the antigens by developing a firm red bump at the site within 2 days.
The TB antigens used in a tuberculin skin test are called purified protein derivative (PPD). A measured amount of PPD in a shot is put under the top layer of skin on your forearm. This is a good test for finding a TB infection. It is often used when symptoms, screening, or testing, such as a chest X-ray, Opens dialog, show that a person may have TB.
A tuberculin skin test cannot tell how long you have been infected with TB. It also cannot tell if the infection is latent, Opens dialog (inactive) or if you have active TB that can be passed to others.
A tuberculin skin test is done to find people who have tuberculosis (TB), including:
- People who have been in close contact with someone known to have TB.
- Health care workers who are likely to be exposed to TB.
- People with TB symptoms, such as an ongoing cough, night sweats, and unexplained weight loss.
- People who have had an abnormal chest X-ray.
- People who have had a recent organ transplant or have an impaired immune system, Opens dialog, such as those with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), Opens dialog.
A tuberculin skin test should not be done for people:
- With a known TB infection.
- Who have had a previous severe reaction to the TB antigens.
- Who have a skin rash that would make it hard to read the skin test.
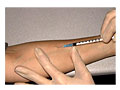
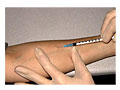
For a tuberculin skin test, you sit down and turn the inner side of your forearm up. The skin where the test is done is cleaned and allowed to dry. A small shot of the tuberculosis antigen (purified protein derivative, or PPD) is put under the top layer of skin, Opens dialog. The fluid makes a little bump (wheal) under the skin. A circle may be drawn around the test area with a pen.
There is a very slight risk of having a severe reaction to the tuberculin skin test, especially if you've had tuberculosis (TB). An allergic reaction, Opens dialog can cause a lot of swelling and pain at the site. You may have a sore.
You cannot get a TB infection from the tuberculin skin test. That's because no live bacteria are used for the test.
A tuberculin skin test is safe during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
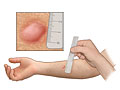
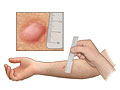
Redness alone at the skin test site usually means you haven't been infected with TB bacteria. A firm red bump may mean you have been infected with TB bacteria at some time. The size of the firm bump, Opens dialog (not the red area) is measured 2 to 3 days after the test to find out the result. Your doctor will consider your chance of having TB when looking at the skin test site.
Results of the test depend on your risk for TB. If you are at higher risk, a smaller bump is considered a sign of infection. People at lower risk for having TB need to have a larger bump to be diagnosed with a TB infection.
Normal (negative results): | No firm bump forms at the test site, or a bump forms that is smaller than 5 mm (0.2 in.) |
|---|---|
Abnormal (positive results): | A firm bump that is 5 mm (0.2 in.) or larger in size suggests a TB infection. |
A positive reaction can usually be seen for about 1 week.
A positive tuberculin skin test doesn't mean you have contagious (active) TB. The test can't tell whether you have active or inactive (latent) TB. It also can't tell the difference between a TB infection and a TB vaccination (BCG vaccination, Opens dialog). More tests—such as a chest X-ray, a sputum culture, Opens dialog, or both—are usually done to see if you have an active TB infection.
Current as of: April 30, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Healthwise education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Current as of: April 30, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Healthwise education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC, disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use. Learn how we develop our content.