Introduction
Embolization for bleeding is usually performed for patients who experience excessive or prolonged bleeding. This most commonly occurs with nosebleeds (epistaxis) but can also occur with abnormal blood vessels within the neck, face, or oral areas. While nosebleeds are very common, most are benign and relatively few will require embolization.
Procedure
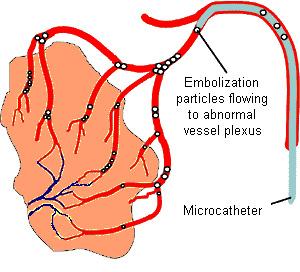
Embolization is performed by placing a small catheter inside the blood vessels that supply the area that is bleeding. Carefully navigating the catheter, under image guidance, to the safest and farthest point, a variety of different materials can then be used to block the bleeding vessels. Materials include liquid tissue adhesives (glues), micro-coils, and micro beads or particles. Embolization therapy can be performed in conjunction with other surgical procedures depending upon the cause of bleeding.